Female Hair Loss Causes
Nearly every women will develop some degree of thinning over their lifetime. Approximately one-third of women will experience noticeable hair loss (alopecia) during their life time. For most, it becomes noticeable after menopause affecting nearly two-thirds of postmenopausal women. While most men expect to experience some noticeable hair loss, most women do not and it can have a significant impact on them socially and their emotional well-being.
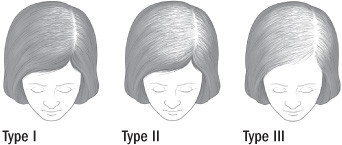
Most women suffer from androgenic alopecia. This is the same kind that affects men, but women are affected differently. Women experience thinning of the part line, followed by diffuse thinning over the top of the head. Unlike men, women rarely experience a receding hairline or go bald.
There are many possible causes for hair loss in women including: physical or emotional stress, medications, medical problems, and genetics. If one notices any unusual hair loss, it is important to see one's Primary Care Provider or Dermatologist to ensure that there are no underlying causes. If one is undergoing emotional difficulties, seeking the help of a therapist or support group may be helpful.
Androgenic alopecia is a result of the action of normal male sexual hormones, called androgens. These hormones play essential roles in both men and women, including sex drive, sexual regulation, and hair growth. Rarely, a tumor may be the cause of excess hormones. In any case, hair loss results from a shortening of the growth (anagen) phase of the hair growth cycle. The amount of time that a hair grows (normally 2-5 years on the scalp) shortens more and more, causing a finer, thinner hair--a process called "follicular miniaturization". The super fine hairs that result are called "vellus" hairs or "peach fuzz", in Layman's terms.
FEMALE HAIR LOSS TREATMENT:
Topical Minoxidil (RogaineTM) for Female Hair Loss:
Minoxidil was initially used for high blood pressure, but was found to regrow hair. It is believed that the medication results in a localized increase in blood flow to the hair follicles, which may be responsible for the increased hair growth and/or thickening of the hairs. Minoxidil now comes in two strengths: 2% and 5%. In general, the application of 5% minoxidil ONCE daily can help some women and is very safe. Results take 2 months to appear and peak at around 4-6 months. For most, a trial of 6-12 months is needed. Less then one-third of users will grow new hair while up to 88% will not lose any more hair. Note: Taking aspirin will reduce the efficacy of minoxidil. When one stops using this medication, progressive hair loss will occur within 12 to 24 weeks and all benefits will be lost.
Oral Minoxidil for Female Hair Loss
Minoxidil taken by mouth has been recently used in very low doses in women with results that are equal to or slightly better than topical minoxidil. Most patients will start with 1.25mg a day and increase very slowly to a dose of 2.5mg a day if needed. It is well tolerated, although can result in unwanted hair growth in other areas.
Anti-androgens for Female Hair Loss:
Testosterone and other "male" hormones can make hair loss worse in women. Those who take male hormones for other reasons should consider stopping. Those who fail topical minoxidil may wish to try an anti-androgen drug, such as spironolactone (AldactoneTM). This works very well in those with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) who make excess androgens. A women taking this medication cannot and should not get pregnant as a male fetus will have permanent genital abnormalities. While this medication is generally well-tolerated, some will experience weight gain, fatigue, loss of libido, and depression.
Anti-yeast shampoos
These shampoos are used to treat seborreic dermatitis, known as Dandruff, as yeast is believed to be the root cause. Recent studies have shown that using an anti-yeast shampoo, such as Head and Shoulders or Nizoral, twice per week will help hair loss even in those without a history of Dandruff.
Treatments for Female Hair Loss
PRP for Female Hair Loss:
After a simple blood draw, platelets and some plasma from one's own blood is injected into the scalp to stimulate hair growth. Results vary greatly from provider to provider and from one technique to the next, but some will experience up to a 25% improvement and sometimes more. In short, this may not be as effective as other treatments, but this is a great "natural" approach to growing new hair that does not require taking any pills or applying any solutions.
You may read more about PRP by clicking HERE
LED Light Treatment for Female Hair Loss:
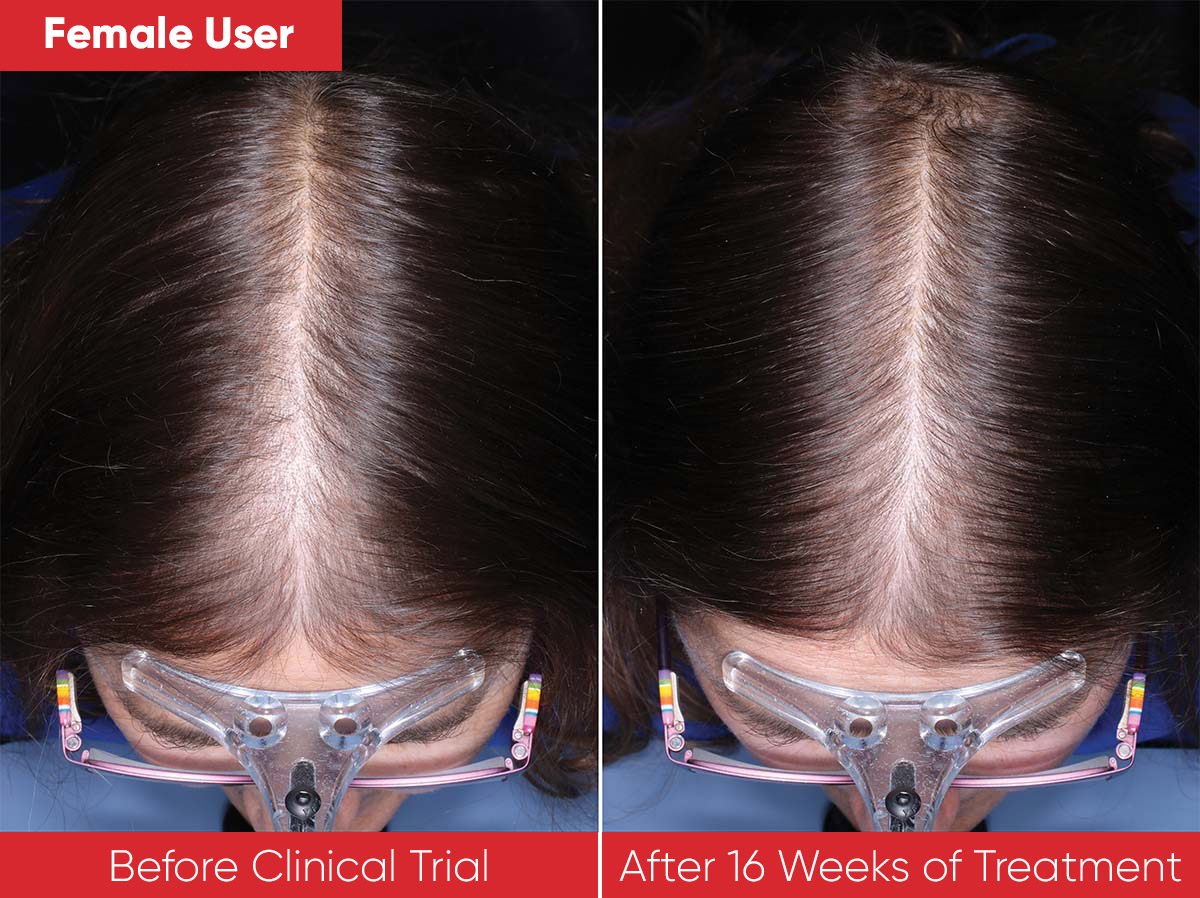
Many devices are now used to treat androgenic alopecia, but they are all not the same. To date, there are no contradictions for LED treatment and no known drug interactions between LED light treatment and other medications used for hair loss. Some believe that light treatment may complement other treatments, such as PRP. Red lights works by increasing blood flow and decreasing inflammation, but again devices differ greatly in both cost and results. Dual wavelength LED light therapy utilizes more than one wavelength (color) and has shown even better results. The added orange light increases nitric oxide in the skin, which slows DHT production. The Revian dual-wavelength system is FDA-approved, has been clinically proven to help regrow hair, and comes with a 6-month money back guarantee.
Iron Supplements to Treat Hair Loss in Women:
While not a common cause of hair loss, iron deficiency contribute. Those with heavy menstrual periods and those who are vegetarians are more at risk for iron deficiency. One can have their iron level checked and, if low, supplements can be given. Those with normal iron levels will not benefit from iron supplementation.
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF HAIR LOSS
Hair Transplantation in Women:
This procedure has been used since the 1950s and has been refined to produce a better result. Most surgeons today perform "follicular unit transplantation", which was first used in the mid-1990s. Results are permanent, although future loss may occur unless one treats the underlying condition as described above.