Actinic keratosis
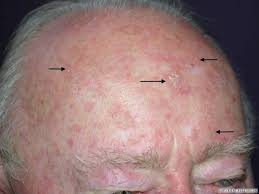
Actinic keratosis (AK or Solar Keratosis) is the most common precancerous condition affecting the skin. In nearly all cases, these lesions form on skin that has been damaged by chronic exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun and/or indoor tanning beds.
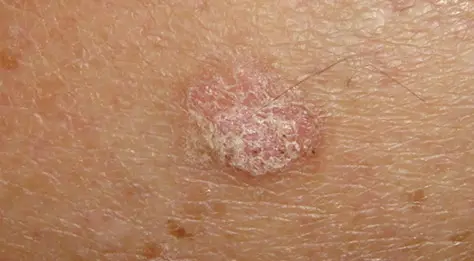
These lesions are often felt better than they are seen, as they feel rough like sandpaper. Lesions can be very small (a couple of millimeters) or larger. Some areas look like scale on a pink base. These lesions do not change much and are often confused with other conditions, such as seborrhea or "eczema".

Do I have to treat these lesions?
No one "has to" treat anything, but that does not mean that it is wise not to do so.
In their current state, these lesions pose no health concerns. They do not resolve on their own and only worsen with time. If left untreated, these precancerous lesions may evolve into an invasive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) or a squamous cell carcinoma in situ prompting more aggressive treatment. Invasive tumors can metastasize (spread) to the lymph nodes or other organs.
Therefore, in healthy patients it is highly advisable to treat these lesions. Considering treatment is simple and not very costly, there is very little downside to doing so in nearly all cases.
What treatments are available?
Here are the most common treatments used today:

Cryosurgery
Individual lesions are frozen using liquid nitrogen using a spray gun or a cotton-tipped applicator. While this is effective, this can leave hypo-pigmented (lighter) spots at the treated area, which can be permanent. Less commonly, hyper-pigmented (darker) spots can appear. If this occurs you should inform your doctor immediately as this can be treated using creams if treated early.
Sun avoidance after treatment will reduce the risk of darkening greatly. The cure rates for this option are between 39 and 83%.
In nearly all cases, only individual lesions of actinic keratosis are treated. Subclinical damage that cannot be seen by the naked eye are left untreated.
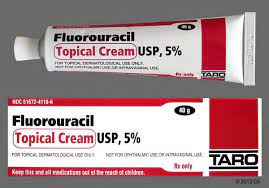
5-Fluorouracil cream (5FU, Efudex, Carac)
5-Fluorouracil cream (5FU) is an effective treatment and has been used for many decades. This topical chemotherapy drug destroys the atypical cells. Treatments are often 2-4 weeks. When used alone, redness and scabbing is very common and not pleasant. This treatment alone has cure rates of approximately 62%.
"The Harvard Regimen": This cream can be used with calcipotriene, a cream that is similar to Vitamin D3. By using both calcipotriene and 5-FU, there is very little irritation, the treatment is much shorter (5-7 days), the cure rate is better, and the results last longer than with 5-FU alone.
Dr. Bader prefers this two drug regimen over any other field treatment due to its low cost and good cure rates. He likes to treat areas/zones and not individual lesions, as nearly everyone has “subclinical lesions”–damage that are not seen or felt, but are there. By doing so, one will have less actinic keratosis and a lower risk of skin cancer in the treated area for many years.
Many insurance plans will not cover these drugs or charge a high copay. Dr. Bader can have this medication compounded at a pharmacy for as little as $35, which is very cost effective.
Imiquimod
Imiquimod is a cream that revs up the body’s immune system so that one’s own body will recognize the atypical cells and destroy the atypical cells. This results in scabbing and crusting during treatment, which can last several weeks. Dr. Bader prefers this treatment in patients are prone to squamous cell carcinoma in situ and superficial basal cell carcinoma, as this cream is often effective against those as well. Similar to 5-FU, regions or areas can be treated and not just lesions themselves. This cream was very expensive until recently and can now be purchased for under $30 using a savings card, such as that from www.goodrx.com. In most cases, Dr. Bader recommends treating affected areas and not just lesions. By doing so, one will have less actinic keratosis and a lower risk of skin cancer in the treated area for many years.
The cure rates are very good as most achieve a 82% reduction of lesions.
INGENOL MEBUTATE (Picato)
Ingenol mebutate (Picato) is one of the newest topical treatments available for actinic keratosis. It is available in two strengths-one for the face and scalp (0.015%) and one for the rest of the body (0.05%). It is applied once a day for 2-3 days on the face and scalp and once a day for 2 days on the other areas.
The main advantage of treatment is that it only need be applied 2-3 times over a few days. The major disadvantages are cost, which is over $1000, and irritation, which peaks at day 4 and may take 2 weeks to resolve.
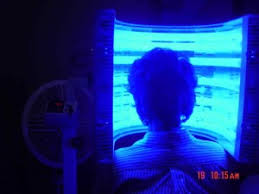
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) is a field treatment as individual lesions are generally not treated, but the entire area. Patient will have a medicine applied to the lesions or region where there is sun damage. After waiting approximately one hour, one will go under a blue or red light (literally a light that is blue or red) for approximately 16 minutes. There is slight to moderate burning during this time, which activates the medication. Some mild crusting and swelling may occur over the next few days. Thicker and/or deeper lesions typically do not respond well. The cosmetic results are excellent.
This treatment is typically more expensive than other options and most profitable for the provider, which is why many Dermatologists are utilizing this method more than ever before. The main advantage to this treatment over topical medications is that the patient does not need to do anything, other than avoid sun exposure for one day following the procedure. Everything is done in the office.
In most cases, Dr. Bader prefers 5-FU & calcipotriene ("Harvard Regimen"), which has results that are at least as good, if not better than PDT, is far less expensive, and has irritation that is similar or less than that seen with PDT.